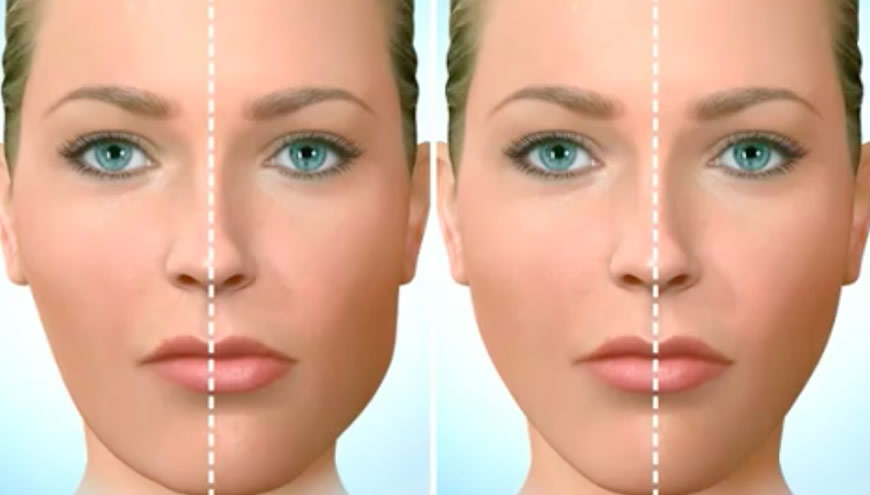
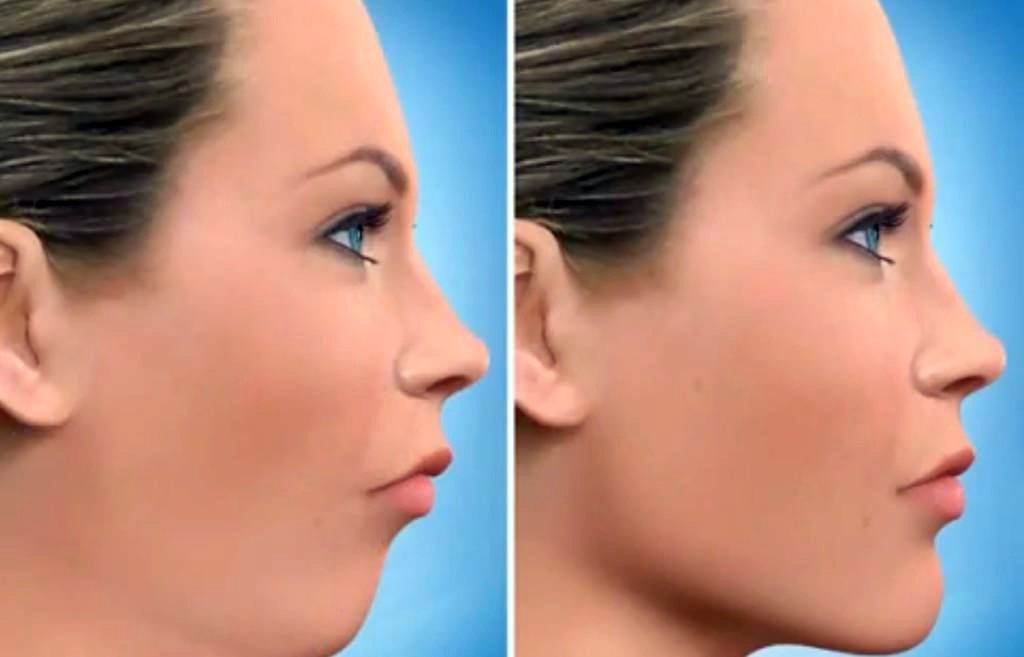
What is Orthognathic Surgery?
Orthognathic surgery is the surgical correction of the jaws to restore proper anatomy, function, and facial proportions. It helps achieve a normal bite, improve facial symmetry, and alleviate breathing problems, including obstructive sleep apnoea.
Who is it suitable for?
Orthognathic surgery is indicated when there are:
Significant abnormalities in the size or position of the jaws or in the bite,
Facial asymmetry,
Obstructive sleep apnoea that can be treated by advancing the jaws forward.
How the procedure is performed
Before surgery, a thorough diagnostic assessment is carried out, including a clinical examination, X-rays, and bite evaluation.
Orthodontic treatment is often required both before and after surgery.
The operation is performed under general anaesthesia through small incisions inside the mouth, leaving no visible scars.
The jawbones are cut into segments, repositioned correctly, and fixed in place with titanium plates and screws.
Titanium plates are biocompatible and do not need to be removed.
Recovery and results
After surgery, patients usually stay in the hospital for 2–3 days.
A liquid diet is recommended for the first 2 weeks.
The stitches are dissolvable and do not require removal.
Most patients can resume normal daily activities within 7–10 days.
The final result is a correct bite, improved facial symmetry, and wider airways for easier breathing.